Case Study: How YSZ Enhanced ZSBN Nozzle Durability
Introduction
This case study outlines how Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) addressed a client's need for longer-lasting ZSBN nozzles in high-temperature, high-wear environments. Through adjustments in both ceramic formulation and forming parameters, we delivered a solution that improved resistance to abrasion and thermal degradation, without significantly raising cost.
Background
ZSBN (Zirconia Strengthened Boron Nitride) nozzles are commonly used in thermal spray, molten metal handling, and other industrial processes where both heat and wear are constant challenges. One of our clients reported that their existing nozzles, based on standard ZrO2-reinforced BN, were falling short in terms of service life. Failures occurred at operating temperatures exceeding 1000 °C and in systems with fast-moving abrasive media. Frequent nozzle replacements led to downtime and higher maintenance costs.
The client originally used a formulation with unstabilized zirconia. Our task was to enhance durability under real-world conditions, particularly under cyclic thermal and mechanical loads.
Core Challenge
The primary issue was premature wear and thermal cracking of the nozzle material. While BN provides lubricity and thermal resistance, the original additive system lacked sufficient phase stability and mechanical toughness at elevated temperatures. A more thermally robust reinforcement phase was needed, without introducing brittleness or compromising machinability.
Evaluated Solutions
Option 1: Retain original zirconia additive, adjust pressing process
-
Pros: Minimal change to raw material sourcing or firing profile
-
Cons: Limited gains in thermal or wear resistance
Option 2: Replace with yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ)
-
Pros: Improved high-temp stability, better wear resistance, stronger grain boundary integrity
-
Cons: Slightly higher material cost; requires revised mixing and sintering protocols
Option 3: Apply protective coatings to the nozzle surface
-
Pros: Surface-level abrasion protection
-
Cons: Complex manufacturing, coating may delaminate at high temperature, increased cost
Selected Approach: Option 2 – Replace standard zirconia with 3 mol% YSZ, combined with minor forming process optimization.
Solution & Implementation
We introduced 3 mol% YSZ as the reinforcement phase within the BN matrix. YSZ provides excellent phase stability above 1000 °C and helps slow crack propagation under load. In addition to the material change, we modified the cold isostatic pressing (CIP) stage:
-
Pressing time: Increased hold time from 30 s to 60 s
-
Powder feedstock: Switched to higher-density YSZ-BN composite powder blend
-
Sintering: Maintained the original schedule to avoid extra energy cost
These changes helped achieve better green density and, ultimately, more consistent sintered microstructure.
"We focused on subtle but effective improvements: better particle packing, a more stable reinforcing phase, and tighter control in forming. The results were immediate," said Lisa Ross, Senior Ceramics Engineer at SAM.
Results & Feedback
Performance Metrics
| Property | Original Nozzle | Optimized Nozzle | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
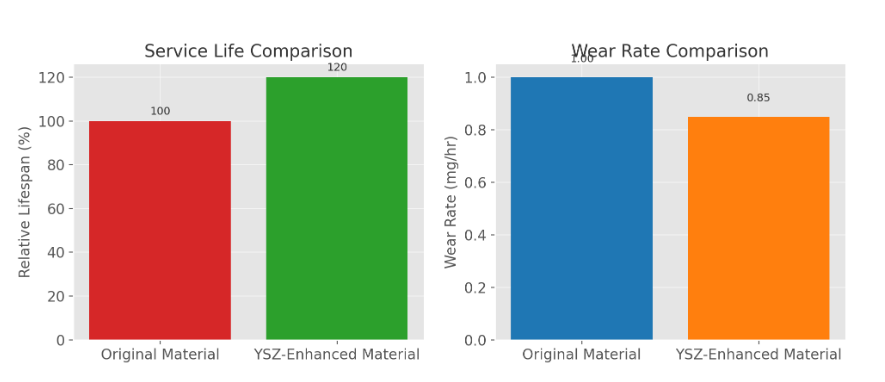
| Wear resistance (relative) | 100% (baseline) | ~112–115% | +10–15% |
| Thermal stability (>1000 °C) | Moderate | High | Significantly better |
| Service life in application | ~40 operating hours | ~48–50 operating hours | +20–25% |
Client Feedback
The customer reported a 20–25% increase in nozzle service life under identical process conditions. Maintenance intervals were extended, and unplanned downtime was reduced. The client approved the new formulation for expanded use across two additional production lines.
"The upgraded nozzles helped us stabilize our spray system and reduce unscheduled stops. It's a meaningful improvement." – Client production manager
Recommendations & Future Work
-
Adopt YSZ-based formulation for production nozzles
-
Continue monitoring long-term performance under varied load cycles
-
Evaluate effect of sintering temperature optimization in future batches
SAM will remain in close collaboration with the client to fine-tune material properties as needed and provide technical support for scaling up the improved nozzles.
Conclusion
This project demonstrates how focused material substitutions—paired with practical forming adjustments—can unlock real-world durability gains. By replacing conventional zirconia with YSZ and increasing pressing hold time, Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) improved both thermal and mechanical performance of the ZSBN nozzle system.
The result: extended service life, better resistance to harsh process conditions, and lower total cost of ownership for the customer.
Have any questions or need a detailed discussion on your specific needs? Send us an inquiry to receive professional solutions and guidance.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us



 Chin Trento
Chin Trento