SAM Showcases HBN for Thermal Management in Power Electronics
Introduction
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM), a trusted name in advanced ceramics and engineered materials, is pleased to highlight the growing success of its high-purity hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) in solving thermal management challenges in high-voltage electronic systems. The material is gaining attention as a reliable solution for demanding applications in electric vehicles, semiconductor devices, and power modules.
Dr. Samuel R. Matthews, Chief Materials Officer at SAM, explains,
“Hexagonal boron nitride offers a rare combination of thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, which makes it ideal for next-generation power electronics. In one recent case, a global client achieved a 40% boost in heat dissipation efficiency after integrating our BN sheets. This is exactly the kind of performance and sustainability advantage SAM is committed to delivering.”
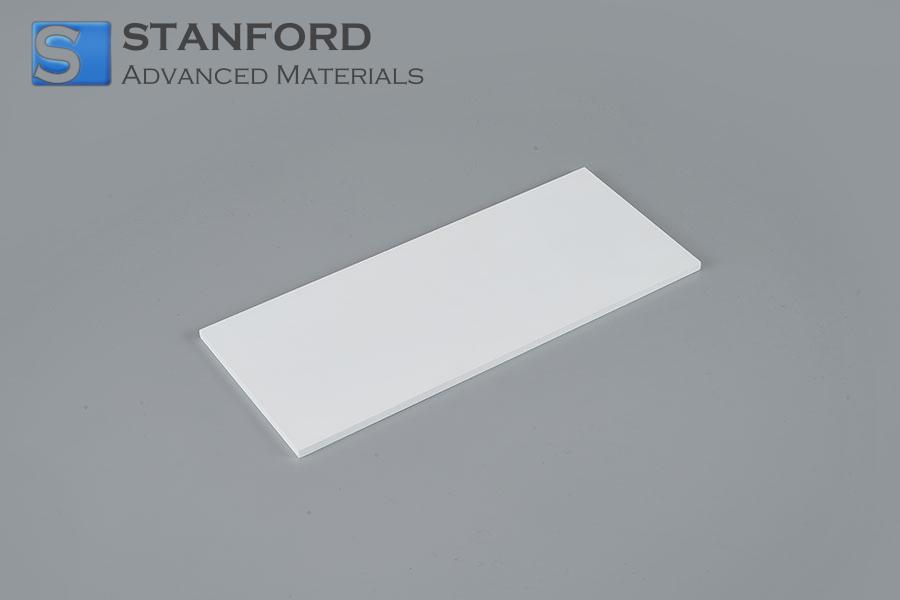

Case Study: Thermal Management in Power Electronics with Hexagonal Boron Nitride
--The Thermal Management Challenge
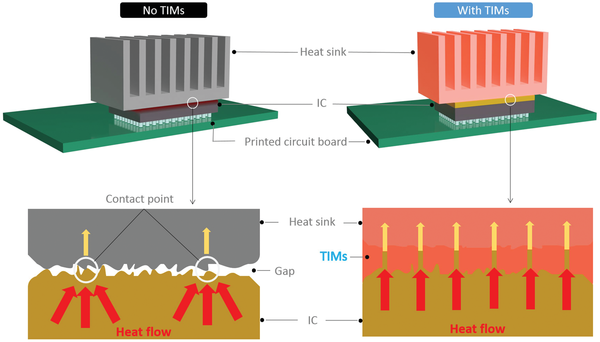
A global manufacturer of silicon carbide (SiC) power modules approached SAM with a critical issue: their existing thermal interface materials were failing in high-temperature applications. The modules, designed for electric vehicle inverters and industrial motor drives, regularly operated above 300 °C. Under these conditions, the customer observed:
- Rapid degradation of thermal interface materials
- Inadequate dielectric insulation at voltages above 3,000 V
- Delamination and warping of ceramic substrate stacks
- Reduced thermal dissipation efficiency, causing local overheating
Their engineering team sought a material that would provide both high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, with stable performance up to at least 900 °C in air. The material also needed to be available in 50 mm × 50 mm × 1 mm sheets, with tight dimensional tolerance and machinability for custom module designs.
 [1]
[1]
--SAM’s Solution: Grade A Hexagonal Boron Nitride
After reviewing the application requirements, Stanford Advanced Materials recommended its Grade A Hexagonal Boron Nitride sheet, a high-purity ceramic engineered for extreme thermal and electrical conditions. Unlike traditional interface materials, h-BN offers a rare combination of thermal conductivity and electrical resistivity, making it ideal for high-voltage applications.
Here are the Product Specifications:
|
Property |
Specification |
|
Purity |
99.5% |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
~35 W/m·K (in-plane) |
|
Electrical Resistivity |
>10¹³ Ω·cm |
|
Dielectric Strength |
>3.5 kV/mm |
|
Operating Temperature |
900 °C in air, 1800 °C in inert gas |
|
Density |
~2.1 g/cm³ |
|
Dimensions Supplied |
50 mm × 50 mm × 1.0 mm |
|
Machinability |
Excellent (suitable for CNC) |
SAM also provided custom machining support and vacuum-sealed packaging to ensure material integrity during shipping and storage.
--Implementation and the Results
The manufacturer integrated the h-BN sheets into their power module assembly, using them as thermal interface layers between the SiC chips and the copper heat spreaders. Post-implementation testing and field data demonstrated immediate improvements:
- A 40 percent increase in thermal dissipation efficiency compared to the previous interface material
- A 20 °C reduction in peak hotspot temperatures under full load
- Zero dielectric breakdown after 1,000 thermal cycles between 25 °C and 300 °C
- Consistent sheet flatness within ±0.02 mm, eliminating mechanical stress during bonding
- Shorter integration time due to excellent machinability
Following these results, the client transitioned their full line of high-voltage SiC modules to SAM’s h-BN solution and initiated a second phase of material evaluation for h-BN coatings in other thermal-critical components.
What’s Hexagonal Boron Nitride?
Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) is a synthetic ceramic compound with a structure similar to graphite. However, unlike graphite, which is electrically conductive, hexagonal boron nitride is an excellent electrical insulator. This fundamental difference gives h-BN a unique profile: it combines high thermal conductivity with electrical resistivity—two characteristics rarely found together in a single material.
Its high purity forms, especially those exceeding 99% BN content, are particularly valued in high-tech manufacturing, electronics, aerospace, and energy sectors. Key physical properties of high-purity hexagonal boron nitride include:
|
Features |
Values |
|
Thermal conductivity |
~30–50 W/m·K (in-plane) |
|
Electrical resistivity |
>10¹²–10¹³ Ω·cm |
|
Dielectric strength |
>3.5 kV/mm |
|
Operating temperature |
Up to 1000 °C in air, and up to 1800 °C in inert atmospheres |
|
Low coefficient of friction |
~0.15 |
|
Density |
~2.1 g/cm³ |
|
Machinability |
Excellent, comparable to soft metals |
Applications of Hexagonal Boron Nitride
Hexagonal boron nitride's unique thermal and electrical properties make it valuable across multiple industries. It is available in various forms—powders, sheets, coatings, and composites—each suited to specific needs.
- h-BN is used as a thermal interface material in SiC/GaN power modules, LEDs, and high-frequency PCBs. It helps dissipate heat while insulating electrically, and it’s also used in EMI shielding and heat spreaders.
- Thanks to its stability, h-BN lines crucibles for metal processing and handles temperatures over 1700 °C in vacuum or inert environments.
- As a dry lubricant, h-BN performs well under pressure and heat, making it ideal for aerospace and vacuum systems.
- In skincare and makeup, h-BN adds a smooth feel, controls oil, and is gentle on the skin.
- It boosts strength, heat resistance, and thermal conductivity in composites, supporting aerospace and defense 3D printing applications.
Conclusion
Hexagonal boron nitride in solving advanced thermal and electrical challenges in power electronics. With a deep inventory of ceramic materials and application-specific support, Stanford Advanced Materials continues to serve as a trusted partner to engineers pushing the limits of performance and reliability.
Reference:
[1] Wang, Zhengfang & Wu, Zijian & Weng, Ling & Ge, Shengbo & Jiang, Dawei & Huang, Mina & Mulvihill, Daniel & Chen, Qingguo & Guo, Zhanhu & Jazzar, Abdullatif & He, Ximin & Zhang, Xuehua & Xu, Ben. (2023). A Roadmap Review of Thermally Conductive Polymer Composites: Critical Factors, Progress, and Prospects. Advanced Functional Materials. 33. 10.1002/adfm.202301549.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators
 Write for Us
Write for Us


 Chin Trento
Chin Trento