Neodymium: Element Properties and Uses
Description
Neodymium is a rare-earth metal with unique magnetic and physical properties; this post covers its introduction, uses, preparation, and industrial products.
Introduction to the Element
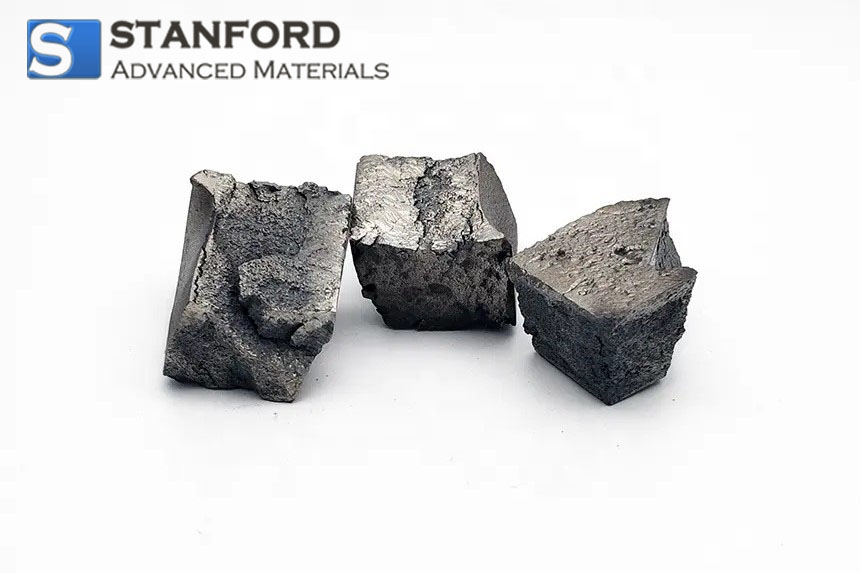
Neodymium is a member of the lanthanide series, a group of fifteen metallic elements in the periodic table. Discovered in the late 19th century, neodymium has gained recognition for its lustrous, silvery appearance and remarkable versatility. As one of the key rare-earth elements, it is widely used in various high-technology applications.
Chemical Properties Description
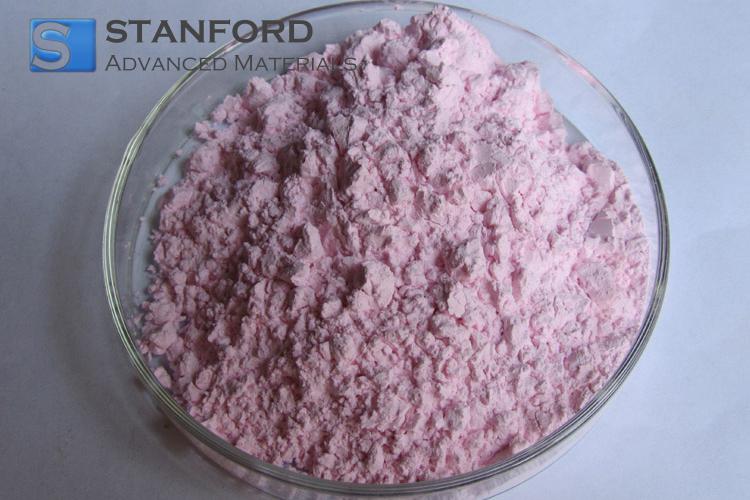
Neodymium displays a set of chemical properties that set it apart from many other metals. Predominantly found in a +3 oxidation state, it forms compounds such as neodymium oxide and neodymium chloride. In its pure form, neodymium is highly reactive when finely divided, readily forming an oxide layer upon exposure to air. This reactivity is exploited in the synthesis of various compounds used in pigments, catalysts, and specialized alloys.
Physical Properties Data Table
|
Property |
Value |
Unit |
|
Atomic Number |
60 |
- |
|
Atomic Weight |
144.24 |
amu |
|
Melting Point |
1,024 |
°C |
|
Boiling Point |
3,074 |
°C |
|
Density |
7.01 |
g/cm³ |
|
Electrical Resistivity |
64 |
nΩ·m (at 25°C) |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
16.5 |
W/m·K |
|
Crystal Structure |
Hexagonal |
- |
Magnetic Properties of Neodymium
|
Property |
Value |
Unit |
|
Magnetic Ordering |
Paramagnetic (bulk) |
- |
|
Curie Temperature |
~310 |
°C |
|
Saturation Magnetization |
~1.6–1.7 |
T (Tesla) |
|
Coercivity (NdFeB magnets) |
High |
- |
|
Remanence (NdFeB magnets) |
~1.0–1.4 |
T (Tesla) |
|
Maximum Energy Product (NdFeB) |
200–400 |
kJ/m³ |
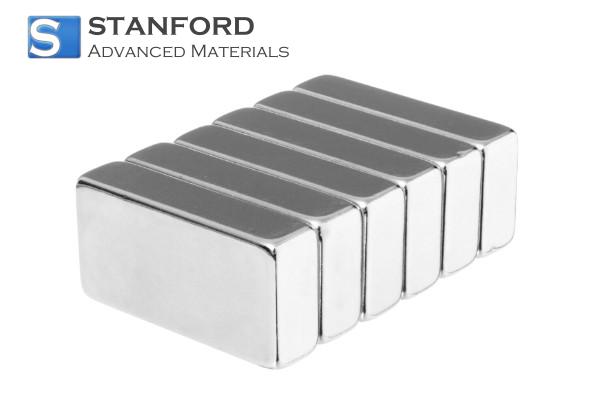
Neodymium is best known for its role in neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets. For more information, please check Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM).
Common Uses
Neodymium is perhaps best known for its application in producing high-strength permanent magnets. Neodymium magnets rank among the strongest available and are a critical component in electric motors, computer hard drives, and audio equipment. Their powerful magnetic field and compact size have revolutionized the design of many modern devices.
Beyond magnets, neodymium is used in the manufacture of lasers, particularly in solid-state laser systems. These lasers find applications in medical devices, cutting tools, and various research instruments.
Preparation Methods
The preparation of neodymium involves sophisticated extraction and purification techniques. Typically, neodymium is obtained from ores such as monazite and bastnaesite. The extraction process begins with chemical treatment of the ore, followed by solvent extraction procedures that separate neodymium from other rare-earth elements.
After extraction, further refining is achieved through precipitation and ion exchange methods. Reduction processes are then applied to produce neodymium in its metallic form.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is neodymium?
Neodymium is a rare-earth element known for its significant role in high-performance magnets and advanced technological applications.
How are neodymium magnets utilized?
Neodymium magnets are used in electric motors, computer hard drives, and audio systems because of their exceptional strength and compact size.
What are the main chemical properties of neodymium?
Neodymium typically exists in a +3 oxidation state and forms various compounds such as oxides and chlorides, demonstrating notable reactivity.
How is neodymium extracted from its ores?
Extraction involves chemical treatment of ores like monazite and bastnaesite, followed by solvent extraction, precipitation, and refining processes.
Which industrial products benefit from neodymium?
Products such as high-strength magnets, solid-state lasers, advanced ceramics, and specialized optical components rely on neodymium for their unique properties.

 Bars
Bars
 Beads & Spheres
Beads & Spheres
 Bolts & Nuts
Bolts & Nuts
 Crucibles
Crucibles
 Discs
Discs
 Fibers & Fabrics
Fibers & Fabrics
 Films
Films
 Flake
Flake
 Foams
Foams
 Foil
Foil
 Granules
Granules
 Honeycombs
Honeycombs
 Ink
Ink
 Laminate
Laminate
 Lumps
Lumps
 Meshes
Meshes
 Metallised Film
Metallised Film
 Plate
Plate
 Powders
Powders
 Rod
Rod
 Sheets
Sheets
 Single Crystals
Single Crystals
 Sputtering Target
Sputtering Target
 Tubes
Tubes
 Washer
Washer
 Wires
Wires
 Converters & Calculators
Converters & Calculators




 Chin Trento
Chin Trento